What is a magneto ignition system, and why is it crucial in powering engines? This self-contained system generates electric current without needing an external source, making it a vital component in small engines and older vehicles. Curious about how it works and why it’s still relevant today? Keep reading to uncover its mechanics and significance.
What Is Magneto Ignition System
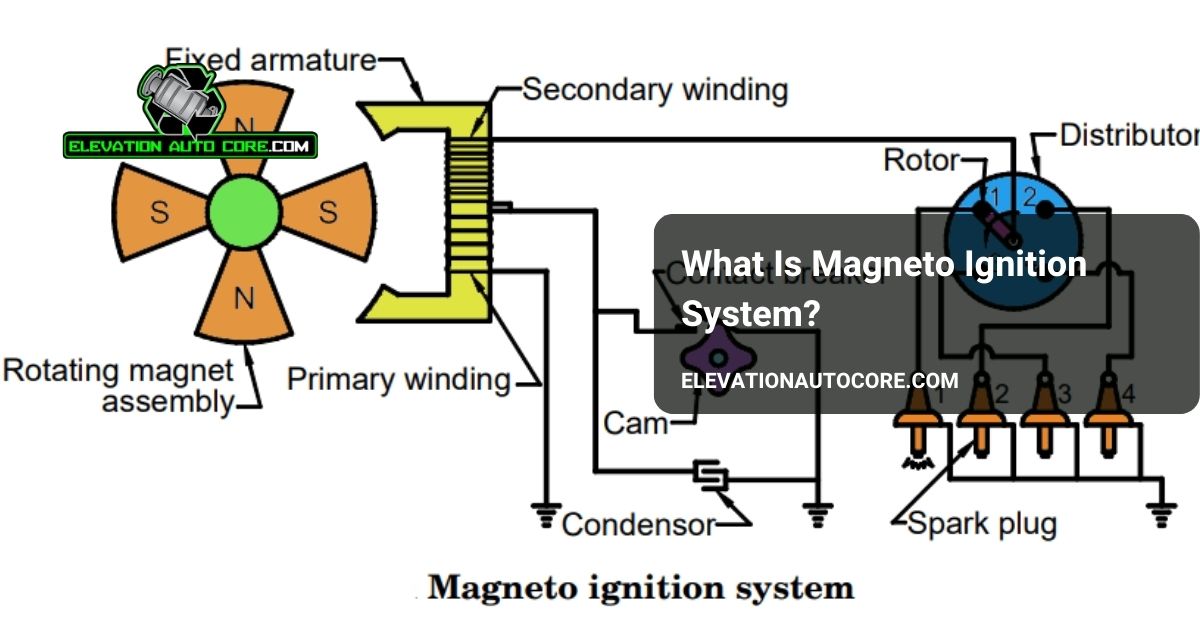
A magneto ignition system is a self-contained unit that generates electricity to ignite the air-fuel mixture in an engine. Unlike battery-powered systems, it doesn’t rely on an external energy source. Rotating magnets within the system produce electricity through electromagnetic induction.
You often find this system in small engines like motorcycles, chainsaws, and lawnmowers. Vehicles and equipment that operate in remote areas also use it due to its independence from external power. Its compact and robust design ensures reliable performance in demanding conditions.
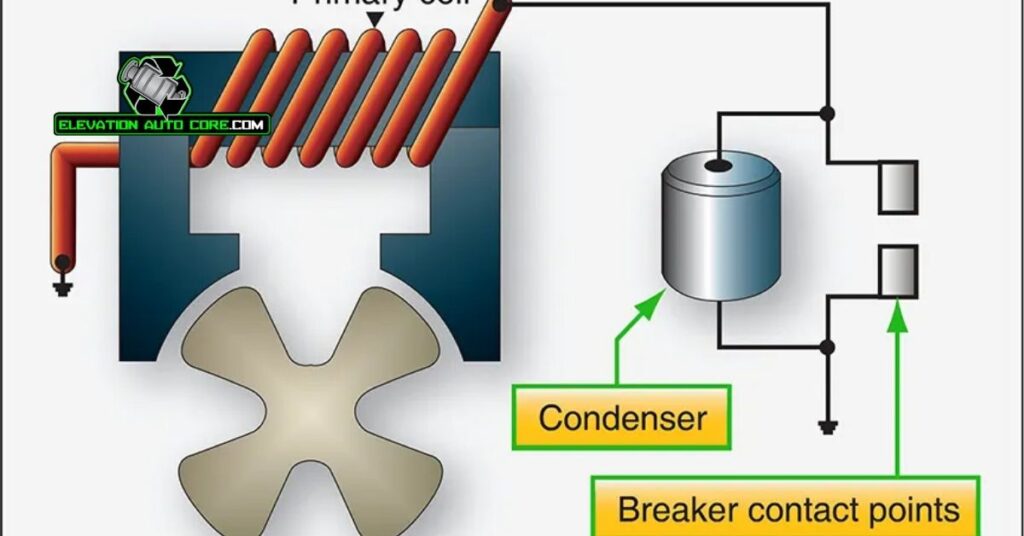
Components of this system include a magnet, coil, condenser, and contact breaker. The magnet produces a magnetic field, while the coil generates a high-voltage current. The condenser suppresses electrical arcing, and the contact breaker controls the current’s flow.
This ignition method provides exact advantages, especially for engines that need consistent spark generation without external dependency. Compact dimensions make it functional for applications where battery maintenance isn’t feasible.
Components Of A Magneto Ignition System

A magneto ignition system relies on several key components working together to produce a spark for engine ignition. Each part plays an integral role in ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
Magnet
Magnets supply the magnetic field necessary for electricity generation. Positioned within the magneto, they rotate to induce an electric current in the coil. For optimal performance, these magnets often have high magnetic strength and precise alignment, which allows consistent energy transfer.
Coil
The coil amplifies the electrical energy generated by the magnet. Consisting of primary and secondary windings, the coil steps up the voltage to a level necessary to create a spark. Primary windings carry the low-voltage current while secondary windings boost it to a high-voltage output required by the spark plug.
Distributor
Distributors direct the high-voltage current from the coil to the spark plug. Used in multi-cylinder engines, this component ensures each cylinder receives the spark in the correct sequence. Timing mechanisms within the distributor help maintain synchronized engine operation.
Spark Plug
Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture by generating a spark at the right time. Connected to the distributor or directly to the coil, they transfer the high-voltage current into the combustion chamber. Durable materials, like ceramic insulators and metal electrodes, enhance their reliability and lifespan.
How Magneto Ignition System Works

A magneto ignition system operates by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to ignite the engine’s air-fuel mixture. Its functionality relies on precise energy generation, spark timing, and an efficient ignition process.
Energy Generation
The magneto creates electrical energy using rotating magnets and electromagnetic induction. When magnets attached to a rotating flywheel move past a coil, they induce an electrical current. This process produces a high voltage necessary to generate a spark. Reliable energy generation depends on the strength of the magnet and the alignment of the coil.
Spark Timing
Spark timing ensures the spark occurs at the optimal point in the engine’s cycle. The contact breaker regulates the timing by interrupting the primary circuit. As the circuit breaks, a sudden collapse in the magnetic field induces a high voltage in the secondary winding. Precise timing maximizes combustion efficiency and engine performance.
Ignition Process
The ignition process begins when the high-voltage current reaches the spark plug. This current jumps across the spark plug gap, creating a spark that ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinder. Proper ignition relies on the spark plug’s design and durability, ensuring consistent performance under varying conditions.
Types Of Magneto Ignition Systems
Magneto ignition systems come in different configurations, each designed to suit exact engine requirements. The two most common types are the rotating magnet type and the rotating coil type.
Rotating Magnet Type
This type features a rotating magnet surrounded by stationary coils. The magnet’s motion produces a changing magnetic field that induces an electric current in the coils. Small engines like motorcycles or chainsaws often use this design due to its simplicity and reliability. Efficient energy generation relies on precise alignment between the magnet and the coils. It provides consistent performance in harsh environments or remote areas.
Rotating Coil Type
With this setup, the coil rotates within a stationary magnetic field. This rotation generates the electric current necessary for ignition. Larger engines often benefit from this type as it delivers a higher voltage output. Ensuring proper insulation of the rotating coil is critical to avoid energy loss or overheating. Its design suits applications where engine conditions demand robust ignition capabilities.
Applications Of Magneto Ignition Systems
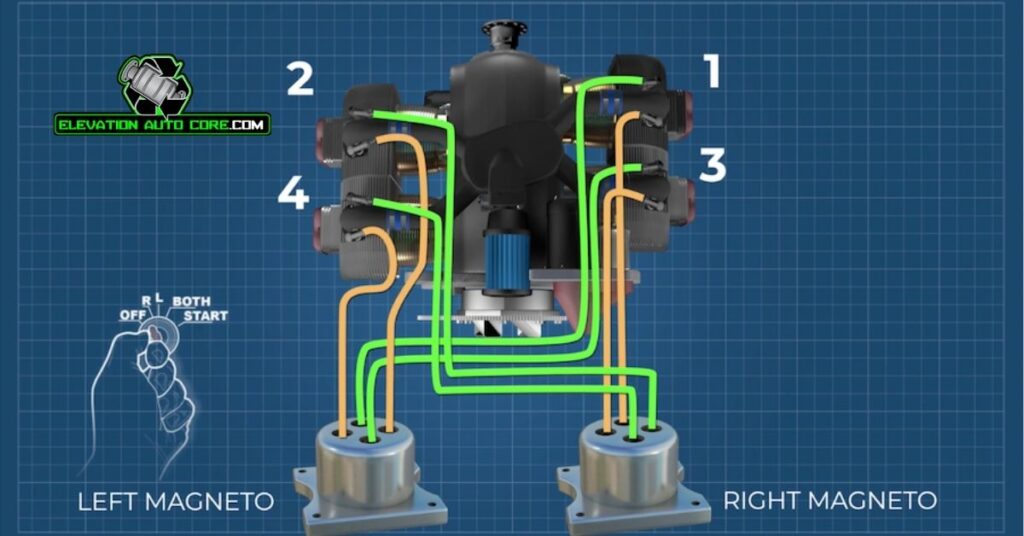
Small engines heavily rely on magneto ignition systems for efficient operation. These engines include motorcycles, chainsaws, and lawnmowers, which require dependable ignition without external power sources. In remote areas, this system proves invaluable by allowing machines to function independently of an electrical grid.
Vintage vehicles often incorporate magneto ignition systems due to their self-sufficiency. Classic cars, tractors, and older aircraft commonly use these systems because of their historical design and minimal maintenance requirements. Their durability makes them a preferred choice in environments where reliability is critical.
High-performance engines also benefit from magneto ignition systems. Racing motorbikes and other specialized vehicles with strict weight and size constraints adopt this system to reduce complexity. The compact design and robust output make it a practical solution for these contexts.
Stand-alone agricultural equipment frequently depends on magneto ignition systems. Devices like portable water pumps, tillers, and generators stand out as examples of machinery requiring consistent ignition performance. This system ensures smooth operation, even in areas where electricity isn’t accessible.
Outdoor power tools depend on this technology for functionality. Equipment such as leaf blowers, trimmers, and portable saws function effectively using magneto ignition due to its reliable spark generation. Their use in tasks away from electrical outlets underscores the system’s importance.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Magneto Ignition Systems
Magneto ignition systems provide several benefits but also have some limitations. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages helps determine their suitability for exact applications.
Advantages
These systems operate without needing an external power source. They generate the necessary spark energy independently, making them highly reliable in remote areas or situations where power access is limited.
Compact design reduces weight and complexity in engine setups. This trait is particularly beneficial for small engines like motorcycles or portable equipment.
Minimal maintenance requirements lower the risk of system failure. The absence of a battery reduces dependency on additional components, improving durability.
High-performance output ensures consistent ignition. This consistency adds reliability, especially in high-speed or rugged operations like racing bikes.
Disadvantages
Initial costs can be higher compared to battery-powered systems. Complex manufacturing processes contribute to these increased expenses.
Lower energy output limits applications in larger engines. Larger engine setups may require more advanced ignition systems for optimal performance.
Maintenance challenges arise in detecting issues. Specialized tools and expert knowledge might be necessary for troubleshooting or repairs.
Irregular performance may occur if components degrade. Worn-out parts, such as coils or contact breakers, can cause weak sparks or delayed ignition timing.
Conclusion
Understanding the magneto ignition system gives you valuable insight into a technology that remains vital for various engines and applications. Its self-sufficient design, reliability, and efficiency make it a preferred choice in many scenarios, especially where external power sources aren’t an option. Whether you’re exploring its role in small engines, vintage vehicles, or high-performance equipment, the magneto ignition system showcases a remarkable blend of simplicity and innovation. By appreciating its components, functionality, and applications, you can better grasp why it continues to be a cornerstone in engine ignition technology.