What is a cylinder head, and why is it so crucial to your engine’s performance? This essential component sits at the top of your engine block, sealing the combustion chamber and housing key parts like valves and spark plugs. Understanding its role can help you appreciate how it impacts efficiency, power, and overall engine health—so let’s immerse.
What Is A Cylinder Head
A cylinder head is a key component of an internal combustion engine. Positioned on top of the engine block, it creates a seal for the combustion chamber. This placement helps maintain compression and allows efficient combustion.
It houses critical parts like valves, spark plugs, and sometimes fuel injectors. Valves control airflow in and out of the cylinders, while spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mix for combustion. These components work together to ensure smooth engine operation.
The design of the cylinder head influences engine performance. Material choice, cooling channels, and port shapes directly affect power output and thermal efficiency. Modern variants often incorporate advanced tech to enhance durability and performance.
Proper functioning of the cylinder head is vital for engine reliability. If the seal or internal components fail, issues like overheating or compression loss may arise. Regular maintenance can prevent common problems associated with cylinder heads.
Functions Of A Cylinder Head

A cylinder head performs essential tasks within an engine, supporting combustion and ensuring efficient energy transfer. It’s designed to affect engine performance, compression, and sealing capabilities.
Role In Engine Performance
The cylinder head directly impacts engine output. It houses components like intake and exhaust valves that regulate airflow and fuel mixture entering and exiting the combustion chamber. Proper valve operation ensures optimal engine power and fuel efficiency.
Cooling channels embedded in the cylinder head help prevent overheating. Heat dissipation is critical for maintaining reliable performance, especially during high-speed or prolonged engine operation.
Material choice, such as aluminum or cast iron, affects thermal handling and weight. Lightweight heads improve fuel economy, while more robust materials handle high-power engines effectively.
Sealing And Compression Responsibilities
The cylinder head creates a tight seal with the engine block to maintain combustion pressure. This seal is achieved using a gasket positioned between the head and block. A secure fit prevents gas leakage and preserves engine efficiency.
Compression depends on the cylinder head’s design. Combustion chambers within the head determine the compression ratio, significantly affecting power output and fuel consumption. Proper sealing and compression ensure the engine runs smoothly, avoiding issues like misfires or power loss.
Components Of A Cylinder Head

A cylinder head incorporates multiple elements that work together to optimize engine performance. These components play key roles in combustion, airflow regulation, and thermal management.
Valves And Springs
Valves allow control of the airflow and fuel mixture into the combustion chamber. Intake valves bring in air and fuel, while exhaust valves expel burnt gases. Springs ensure these valves open and close precisely, maintaining the timing essential for efficient engine operation. Properly functioning valves and springs improve power output and minimize engine wear.
Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber is the confined space where air and fuel ignite to create energy. Its shape and material composition affect the combustion process and thermal efficiency. A well-designed chamber enhances the mixture’s burning, resulting in higher engine performance and reduced emissions. It also withstands extreme temperatures and pressures generated during operation.
Ports And Passages
Ports direct air and fuel into the combustion chamber and guide exhaust gases out. Intake ports optimize airflow, aligning it with the engine’s demands. Exhaust passages ensure gases exit smoothly, reducing backpressure and improving efficiency. Clean, well-maintained ports and passages contribute significantly to overall engine responsiveness.
Types Of Cylinder Heads
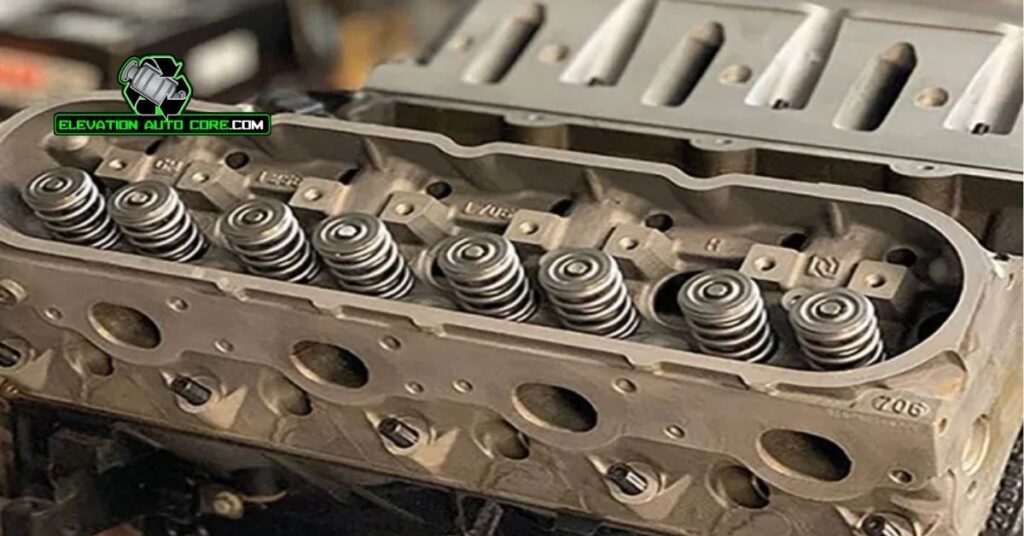
Cylinder heads are classified based on their design and valve arrangement. Each type supports exact engine configurations and performance goals, affecting efficiency and reliability.
Overhead Valve (OHV) Cylinder Head
This design positions the valves above the cylinders. Pushrods link the camshaft to the rocker arms, ensuring precise valve operation. Often found in older or compact engines, OHV cylinder heads are simpler in construction. They provide durability and are typically less expensive to manufacture. But, the design can limit higher-speed performance due to increased mechanical complexity compared to modern alternatives.
Overhead Camshaft (OHC) Cylinder Head
In OHC cylinder heads, the camshaft sits directly above the valves. This eliminates the need for pushrods, resulting in reduced mechanical friction. Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) versions control intake and exhaust valves with one camshaft, while Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC) configurations use separate camshafts for more precise control. OHC heads enhance high-speed engine performance and efficiency, making them a preferred choice in modern automobiles.
Flathead Cylinder Head
Flathead cylinder heads feature an external valve location next to the cylinder. This placement simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces maintenance needs. Although they were widely used in early automotive designs, their inefficiency in airflow and combustion limits their application today. These heads are commonly found in vintage vehicles and low-performance applications.
Common Cylinder Head Problems
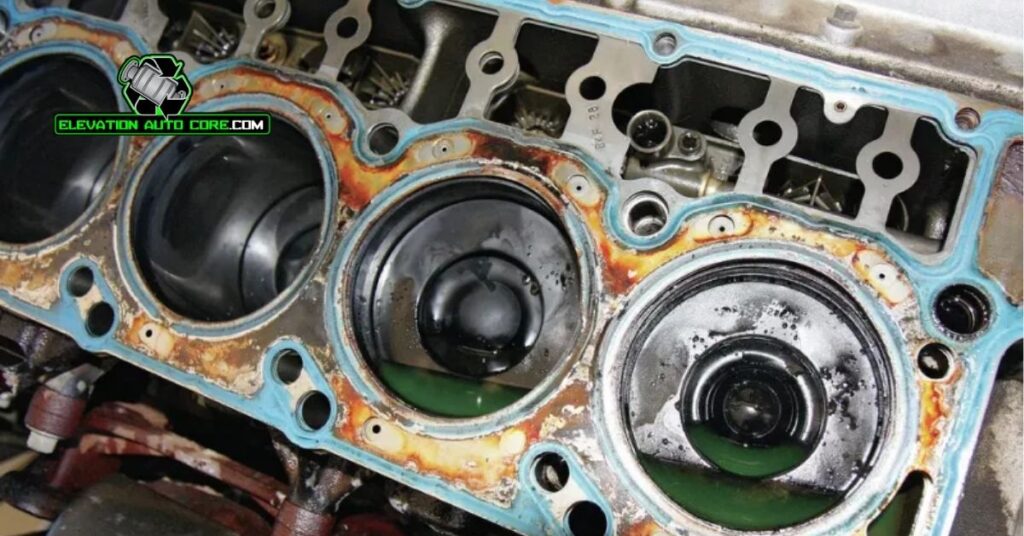

Cylinder head issues can severely affect engine performance and longevity. Addressing these problems early ensures reliability and prevents costly repairs.
Cracks And Leaks
Cracks typically form when the cylinder head is exposed to extreme thermal stress. Rapid temperature changes or overheating usually cause these fractures in materials like aluminum or cast iron. Coolant leaks often accompany cracks, leading to noticeable engine overheating, reduced performance, or contamination in the oil. If left unchecked, cracks compromise the seal between the cylinder head and the engine block, causing combustion gas leakage and pressure loss.
Leaks around valve seats or gasket surfaces may also result from poor maintenance or manufacturing defects. These leaks lead to reduced compression and inefficient engine operation. Visible signs include oil dripping externally and reduced engine oil levels. Regular inspections can quickly detect early leak symptoms.
Warping Issues
Warping mostly occurs due to prolonged overheating or improper torquing of cylinder head bolts. When the head warps, its surface deforms, preventing it from sealing properly against the engine block. This deformity leads to gasket failure, which allows coolant, oil, and gas to mix, severely affecting engine performance.
You might notice symptoms like white exhaust smoke, irregular engine idling, or a important drop in power. Even slight warping impacts valve seating, causing misalignment of airflow paths and combustion inefficiencies. Machining the head or, in severe cases, replacing it often resolves warping problems.
Maintenance And Care For Cylinder Heads
Caring for your cylinder head ensures optimal engine performance and longevity. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs and reduced efficiency.
Regular Inspection
Routine inspections help identify early signs of wear or damage. Look for cracks, leaks, or corrosion on the cylinder head surface, as these can compromise sealing and combustion. Examine the head gasket for signs of failure, such as coolant mixing with oil or exhaust gases seeping into the cooling system. Keep an eye on valve operation and ensure there’s no sticking or unusual noise, which could indicate buildup or wear. Regularly checking for carbon deposits in combustion chambers helps prevent reduced engine output and misfires.
Proper Cooling And Lubrication
Maintaining effective cooling prevents thermal stress and cracking. Ensure the cooling system is functioning correctly by checking coolant levels and inspecting for blockages in passages or hoses. Keep the radiator and water pump in good condition to prevent overheating, especially during prolonged operation. Proper lubrication minimizes friction and prevents component wear within the cylinder head. Use high-quality engine oil and replace it at recommended intervals to avoid buildup and maintain smooth valve train movement. Addressing cooling and lubrication needs extends cylinder head service life and enhances overall engine reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding the cylinder head’s role is essential for maintaining your engine’s performance and reliability. This critical component influences everything from combustion efficiency to thermal management, making it a cornerstone of your vehicle’s operation.
By prioritizing regular inspections and proper maintenance, you can prevent common issues like cracks, leaks, and warping that compromise engine health. Keeping the cylinder head in optimal condition not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of your engine, ensuring a smoother and more efficient driving experience.

